Value Proposition Design: How-To & Example (+ Template)

In this article, you’ll learn how to create value for your customers, bring out the best in your team, and how to work on an idea without wasting time.
Value Proposition Canvas
The Value Proposition Canvas is used to look at who your customer is, what they want to achieve and how your product will help them achieve this:

Don’t feel like reading? This video gives a brief explanation:
- Jobs: what your client is trying to accomplish (‘getting the job done’).
- Pains: describes bad outcomes, risks and obstacles for your customer in getting a ‘job done’.
- Gains: the outcome of what your customer is trying to achieve in concrete benefits.
1.1 Customer Jobs
A ‘Customer Job’ is something your customer is trying to achieve in work or in his life, Jobs are divided into:
- Functional Jobs: the customer is trying to find a solution to a specific problem, such as an air conditioner for the heat, a washing machine for the laundry or a heater for the cold.
- Social Jobs: the customer wants more status or prestige, such as buying branded clothing or purchasing a luxury car.
- Personal/Emotional Jobs: the customer is looking for a certain feeling, such as the feeling of security, joy or safety.
- Supporting Jobs: this helps the customer accomplish a task, such as comparing different products.
It is important to make sure that the different Customer Jobs are broken down by degree of how important they are to the customer.
1.2 Customer Pains
The ‘Customer Pains’ describe what gets in the way of your customer before, during and after getting a ‘Job done’:
- Undesired outcomes, problems and characteristics: functional pains, such as that the solution doesn’t work, that the customer’s status is down or it’s not fun to do.
- Obstacles: things that stop the customer from getting their ‘job done’, such as lack of time or the price of a solution.
- Risks (undesired potential outcomes): what can go wrong, such as losing prestige or getting fired.
Also with the Customer Pains, it is important to subdivide them according to how important they are to the customer.
It is helpful to know exactly how extreme the pain is. The customer may indicate that she does not want to wait for a solution, but then it is up to you to find out the maximum amount of time the customer is willing to wait.
1.3 Customer Gains
With the Customer Gains the outcome and end result is described, these can be divided into 4 different types:
- Required Gains: without this type of gains the solution you offer will not work, a washing machine needs to get your clothes clean.
- Expected Gains: this type of gains is what the customer expects at the very least, even if the solution works without them. For example, a washing machine must be able to run different programs.
- Desired Gains: these are the gains that customers would like and which they could think of themselves. Think for example of the installation of the washing machine in the house.
- Unexpected Gains: these are the gains that go beyond the expectations of the customer, customers would not initially think of. Like not needing detergent in a washing machine.
The gains should also be as concrete as possible, try to express them in numbers. In addition, it is also important to subdivide the gains according to how important they are to the customer.
Common mistakes
The Value Proposition Canvas is not the easiest model to fill out, therefore some common mistakes in the Customer Profile:
- Different customer segments in one profile: create a different Value Proposition Canvas for each type of customer.
- Merge Jobs and Outcomes: jobs are the tasks that a customer tries to achieve and gains are the end results.
- Only focus on functional jobs: obtaining status with a product can be more important than finding the right practical solution.
- Start with a certain bias: you should not be in your head with the solution you want to offer, but go in blank.
- Finding too few jobs, pains and gains: it is important to write down as much as possible and then prioritize it.
- Too vague descriptions: the jobs, pains and gains should be as concrete and clear as possible.
Keep asking as often as possible why your customer gives a certain answer.
Example
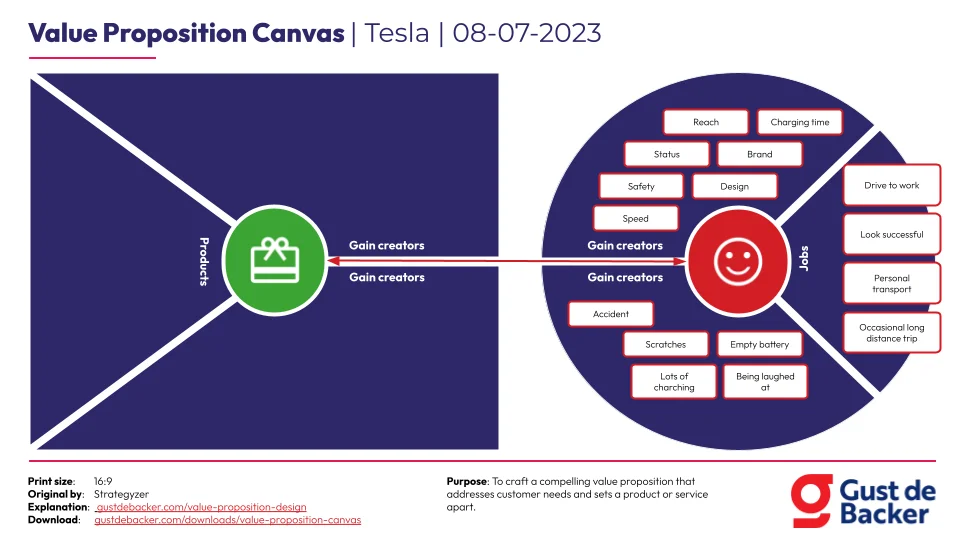
2. Value Map
In the Value Map, you’re going to describe exactly what you offer and how it helps the customer with their ‘Job to be done’:

2.1 Product and Services
This is a listing of everything you offer to the customer, everything the customer might find in your store. There are 4 types of products and services:
- Physical/tangible: physical products.
- Intangible: copyrights or services.
- Digital: music, SaaS or perhaps a platform.
- Financial: such as investments or insurance.
It is important to subdivide your Products and Services based on how important they are to the customer.
2.2 Pain Relievers
The Pain Relievers describe how your product or service is going to take away the customer pain…
It is not necessary to have a specific pain reliever for every pain, but the most important pains should be taken away.
As with all the previous components, it is important to subdivide them based on how important they are to the customer.
2.3 Gain Creators
The Gain Creators describe how your product or service will ensure that the Customer Gains are achieved…
Again, the Gain Creators don’t have to achieve every gain, but they do have to achieve the most important gains.
Make a subdivision based on how important it is to the customer.
Common mistakes
Some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Writing down all your products and services: make sure you only write down the products and services that apply to that specific customer segment.
- Adding products and services to the pain reliever and gain creator fields: the pain relievers and gain creators offer explanations and can be properties of your products and services.
- Offer pain relievers and gain creators that don’t match the pains and gains: the pain relievers and gain creators must match the pains and gains of customer jobs.
- Want to address all pains and gains: it is really not necessary to address all pains and gains in your gain creators and pain relievers.
Example
Download the Value Proposition Canvas:






